Key Factors in Material Performance
Surface finishes refer to the texture or smoothness of a material’s surface after it has been machined or processed. They are critical in determining the functionality, appearance, and performance of a part or component. Surface finishes can range from very rough, with visible tool marks or ridges, to extremely smooth, with a mirror-like appearance. The quality of the finish is often measured in terms of roughness, which is typically indicated in micrometers (µm) or microinches. Common methods to achieve different surface finishes include grinding, polishing, lapping, and honing. Surface finishes play a crucial role in areas such as friction, wear resistance, and sealing in mechanical parts.




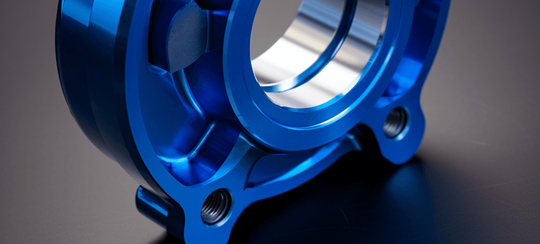
Surface Finishes
Anodizing
In order to overcome the surface hardness, wear resistance and other defects of aluminum alloys, expand the scope of application and prolong the service life, anodizing technology is an indispensable part. During anodizing, the surface of aluminum alloy is usually converted into a layer of oxide film, which has protective, decorative and some other functional characteristics.
However, the machining marks of parts will not be invisible because of the oxide coating. Therefore, we generally recommend that customers should make such parts look beautiful after sandblasting after anodizing.

As machined / Smooth machined
"As machined / Smooth machining" is a surface finishing method. YH-RUSH will machine the surface roughness of the part from Ra6.3 (0.0064mm) to Ra0.2 (0.004mm), usually by milling, grinding, planning, etc. Take this surface processing method generally does not have high requirements for the appearance of the parts, can better control the tolerance, and the cost will also be reduced.

Chrome coating
Chromium metal is extremely easy to passivate in air, and a very thin passivation film is formed on the surface, thus showing the nature of precious metal, and the chromium plating layer has high hardness. Better heat resistance, heated below 500 ℃, its glossiness, and hardness are no significant changes. The friction coefficient of chrome-plated layer is small, especially the dry friction coefficient, which is the lowest among all the metals. So the chrome-plated layer has good wear resistance.

Brushing
Surface brushing is a surface treatment that forms a line pattern on the surface of the workpiece by grinding the product to play a decorative effect. Because the surface brushing treatment can reflect the texture of metal materials, so it has been loved by more and more users and more and more widely used.
Commonly used brushed metals include stainless steel, aluminum and nickel. Brushed finishes are popular in small appliances and white goods, and feature in architectural and automotive designs.

Bead-blasting
The bead blasting process uses high-pressure blasting media beads. The surface can be polished, cleaned, or made rougher to the desired finish by moving the beads along it. Through a high-pressure bead blaster, these beads are shot in the direction of the component. The surface is uniformly "dented" when the beads make contact with it.
Shot blasting gives machined items a consistent matte or satin surface, erasing tool marks and cleaning rusted metal. There are various different grit sizes that show the size of the blasted projectile, and this is largely utilized for visual purposes.

Grinding
Grinding is a machining process that removes material from a workpiece using abrasive tools, such as a grinding wheel. It is commonly used to achieve high precision in dimensions and surface finish, especially in metalworking, ceramics, and glass industries. There are various types of grinding, including surface, cylindrical, internal, centerless, and tool grinding, each suited for specific applications.

Painting
Painting is the process of applying paint or pigment to a surface to create a protective and decorative coating. It is commonly used on materials like metal, wood, and plastic to prevent damage from external factors such as corrosion, moisture, and UV rays, while also enhancing the object’s appearance.
Heat treatment
Heat treatment is a process that modifies the physical and mechanical properties of metals and alloys through controlled heating and cooling. The primary goals are to enhance hardness, strength, toughness, and wear resistance, or to relieve internal stresses. Techniques like annealing, quenching, and tempering are used to achieve desired material properties, ensuring components meet performance standards in various industries.

Don’t miss out on our services!
When you’re ready, we can assist you in selecting the best options for rapid prototyping or production quantities. Reach out to us to start a productive collaboration and find effective solutions together.
Services
All our available services at the moment for you!
CNC Machining
High Precision, Efficiency Flexibility, Repeatability, Reduced Error
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Durability, Versatility Cost-Effective, Lightweight, High Strength
Surface Finishes
Corrosion Resistance, Increased Durability, Enhanced Hardness
